In the fast-evolving world of diagnostic technologies, lateral flow assays (LFAs) have emerged as one of the most critical tools for rapid, point-of-care testing. Whether it’s for detecting infectious diseases like COVID-19, monitoring pregnancy, or testing for allergens, LFAs are known for their convenience, speed, and reliability. But behind every functioning test strip lies a sophisticated manufacturing process—one that relies heavily on precision equipment. Among the most essential pieces of this process is the lateral flow strip cutter.
This blog post explores what a lateral flow strip cutter is, why it’s vital to LFA production, how it works, and what considerations manufacturers should keep in mind when choosing one.
What is a Lateral Flow Strip Cutter?
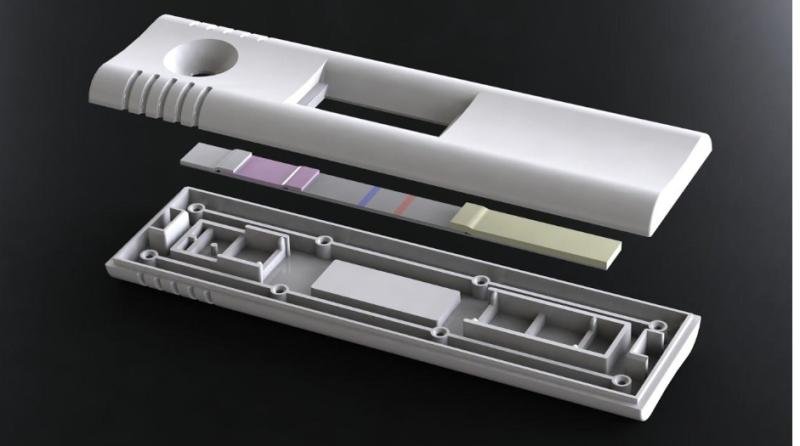
A lateral flow strip cutter is a specialized machine used in the final stages of lateral flow assay production. After the assembly of the assay components onto a backing card—typically including the sample pad, conjugate pad, nitrocellulose membrane, and absorbent pad—the entire structure forms a continuous sheet. This sheet needs to be cut precisely into individual test strips that consumers or healthcare professionals use.
The strip cutter’s job is to slice this large, assembled sheet into narrow, uniform strips without disturbing the alignment or integrity of the layers. Precision is paramount. Even the slightest misalignment or inconsistency can affect the performance and accuracy of the test.
Why Strip Cutting is a Critical Step
Though it might seem like a simple mechanical task, cutting LFA cards into strips is a delicate and mission-critical process. Here’s why:
- Accuracy Affects Test Performance
Each test strip must maintain exact dimensions to ensure the sample flows consistently through the membrane. Even a fraction of a millimeter’s difference can cause variability in test results. - Material Integrity
The cutting process must preserve the structural integrity of each material layer. Any damage to the nitrocellulose membrane or other components can render the test unusable. - Batch Uniformity
In commercial production, thousands or even millions of strips are produced in a single batch. Consistent cutting ensures that every test from that batch meets quality control standards. - Speed and Throughput
High-speed manufacturing environments require a lateral flow strip cutter that can operate quickly without sacrificing precision, ensuring a steady supply of products to market.
How a Lateral Flow Strip Cutter Works
Strip cutters can vary in complexity depending on the production scale, from manual and semi-automatic models to fully automated systems integrated into production lines. However, the fundamental operation remains similar across types:
- Feeding System: The laminated backing card is fed into the machine either manually or via a conveyor.
- Alignment and Registration: Optical sensors and guides ensure the card is correctly aligned before cutting. This prevents miscuts that waste material.
- Cutting Mechanism: Rotary or guillotine blades cut the card into strips with high precision. Some systems allow adjustments in strip width.
- Collection: The cut strips are collected in trays, onto conveyors, or into packaging systems, depending on the integration level.
Some advanced strip cutters include quality control cameras that inspect each strip for alignment, width, and any visible defects.
Manual vs. Automated Strip Cutters
Manual or Semi-Automated Cutters
- Best suited for small-scale or research-based production.
- Offer flexibility for rapid prototyping and testing.
- Lower initial cost but higher per-strip labor cost.
- Typically slower throughput.
Fully Automated Strip Cutters
- Ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
- Integrated with upstream and downstream production lines.
- Reduced labor costs and improved consistency.
- Higher upfront investment but better return over time.
Key Features to Look for in a Lateral Flow Strip Cutter
Choosing the right strip cutter is a significant decision for any LFA manufacturer. Here are some key features and factors to consider:
- Cutting Precision
Look for machines that offer high cutting accuracy, ideally within ±0.1 mm, to ensure test consistency. - Adjustable Width
A good cutter allows for flexibility in strip width, accommodating different test designs. - Material Compatibility
Ensure the machine can handle the types of membranes and backing materials you use, including nitrocellulose, polyester, and other components. - Ease of Integration
For larger operations, integration into existing production lines is a must. Some models offer plug-and-play functionality with conveyors and packaging machines. - Speed and Throughput
Depending on your volume requirements, ensure the cutter can meet demand without bottlenecks. - Maintenance and Reliability
Machines with self-cleaning features, robust blade systems, and minimal downtime are preferable. - Quality Control Systems
Built-in inspection cameras and defect detection systems can help maintain product quality and reduce waste.
Applications Across Industries
Lateral flow strip cutters aren’t limited to one type of diagnostic test. They are used across multiple sectors, including:
- Medical Diagnostics: COVID-19, HIV, malaria, and pregnancy tests.
- Veterinary Testing: Disease diagnostics in animals.
- Food Safety: Allergen detection and bacterial contamination tests.
- Environmental Monitoring: Testing for pollutants and toxins.
- Agriculture: Disease and hormone testing in plants and livestock.
Each of these industries demands reliability and consistency in test performance—requirements that start with precise strip cutting.
Trends and Innovations
As the demand for point-of-care diagnostics continues to grow, so does the need for more sophisticated manufacturing tools. Innovations in lateral flow strip cutters include:
- AI-Driven Quality Control: Integration of artificial intelligence for real-time defect detection.
- Smart Sensors: Enhanced alignment and material tracking.
- Modular Designs: Allowing easy upgrades and adaptation for new test formats.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Reducing material waste during cutting.
These advancements are transforming what was once a basic manufacturing step into a high-tech process that contributes significantly to overall test reliability.
The lateral flow strip cutter may seem like a behind-the-scenes player in the world of diagnostics, but its role is indispensable. As the global demand for accurate, rapid testing continues to rise, manufacturers must invest in quality equipment that ensures every test strip meets rigorous standards.
Whether you’re a startup developing your first LFA or a multinational diagnostics company scaling production, the strip cutter is a piece of technology you can’t afford to overlook. Precision, reliability, and adaptability are the name of the game—and the right strip cutter can help you win it.